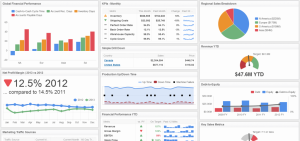
Dashboard
What’s on your dashboard?
If you’re thinking about your trucks & tractors, the answer might be anything from gloves to a coffee mug to a clip for the rifle.
What I mean is “what are you watching on your dashboard?”
- Oil pressure?
- Coolant temperature?
- Exhaust temperature?
- Seeding Rate?
All of these are important, and no doubt they all get significant amounts of your attention.
What are the consequences if any of these go into the RED?
What about your BUSINESS dashboard?
What are the consequences if any of these go into the RED?
Which set of gauges get most of your attention? A failure on which set would be catastrophic?
When I was still farming, the first day of seeding in 2014 had one of these go into the red, only I didn’t know it because the gauge failed. In short, the tractor needed an engine overhaul because of severe overheating. Did it break the farm? No. Did it make seeding extra costly, and take longer than otherwise would? Yes. Did we survive? You betcha.
To Plan for Prosperity
We tend to do what we do best, what we like to do, and what we understand. Understanding the safe range, the limits, and the consequences of oil pressure or coolant temperature running into the red is something that is ingrained into us as youngsters who were imploring that we be able to run equipment. Yet, if no one teaches business owners the safe range, the limits, and the consequences of running their working capital or gross margin “into the red,” how will they know what to watch, or to watch at all?
For an intensive strategy on setting up and monitoring your business dashboard, call or email me anytime.