Direction
Without direction, how do you know where you’re going? And we’ve acknowledged many times in this weekly commentary, if you don’t know where you’re going how would you know if you’ve gotten there?
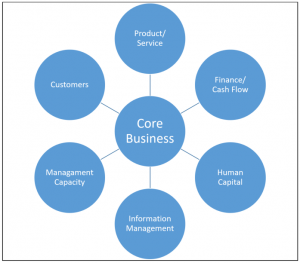
Who sets the direction for your business? Without direction and a charted course, your business is akin to a rudderless boat, just floating along aimlessly. While “floating along aimlessly” sounds like a great vacation, it is most definitely not a strategy for your business.
Direction is set by the leadership team within the business. Big or small, any business without solid leadership, visionary decisive leadership, will find it very difficult to achieve its full potential.
This is why great leaders are well known, highly regarded, and abundantly compensated.
This reality crosses into all aspects of life, not just business. Sports, politics, religion, even in households, the same can be said. Every organization, even volunteer advocacy and/or charity groups have a designated leader…someone who sets the direction for the organization, or in the case where there is a board of directors (or something similar) the leader is accountable for the execution of the strategy and direction for the organization.
Nowhere is the accountability of the leader more public than in professional team sports. Anyone who is fan of any team sport can think of a time where their favorite team, or another team in the league, has went through the turmoil of having a talent laden roster of athletes that habitually fails to succeed. Often, all it takes is a change in leadership, the head coach or general manager for example, and the team begins to win. The leadership can also be identified in the locker room among the players; adding a player with tremendous leadership attributes can be as beneficial as cutting a player who brings a toxicity to the locker room. As fans, we all witness these personnel transactions and then complain or celebrate accordingly (depending on our own view of the matter) but it is a test of the team’s leadership to make the decisions to essentially “fire” a coach or player who may be popular from the outside looking in, but is a detriment from the inside looking out.
This example applies to your business as well. While it may be hard to justify letting go of a star member of your team, if that individual is not conducive to team harmony and progress it falls on the leader to make, or not make, the hard decision. Either way, the leader has provided a clear message to the entire team through their (in)action.
What is even harder is when the person that needs to be let go it the leader himself! Are you holding your team back from achieving their full potential? How would you even know if you are? Could you handle hearing that the problem is you, or would pride get in the way? It is a wise and humble leader who recognizes that the best move for the organization might be to fire herself.
Plan for Prosperity
Whether you believe that leaders are born or leaders are made, an organization without a leader is an organization without direction. Without direction, a business lacks purpose. Without purpose, a business lacks the ability to make progress. Without progress, a business becomes redundant. Look no further than Kodak or Blockbuster Video for real life examples.
As the leader of my own business, I hold the accountability for decisions (good or bad,) results (good or bad,) and overall direction & strategy. As the leader, it is up to me to adapt when things change because, as they say, “The only constant is business is ‘change’.”