Growth Kills
We’ve all heard the anecdote “Speed Kills” as it was used to advise drivers to slow down. Former Canadian Football League (CFL) player Jason Armstead had “speed” and “kills” tattooed on the back of his left and right calf; as one of the fastest players in the league during his playing days, Armstead’s speed as a wide receiver and returner could kill the opposing team’s chances of winning.
But who has ever heard of “Growth Kills”?
I have written about it in this commentary and spoken about it at industry events: business can grow itself to death.
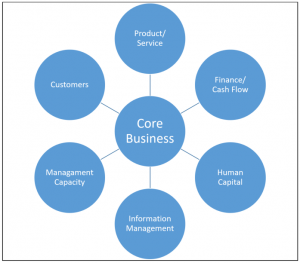
When a business pursues expansion at a pace that exceeds:
- Management’s ability to manage the growth,
- The business’ ability to finance the growth, or
- The market’s ability to consume the growth…
…we have an entity that has likely grown itself to bankruptcy, or the very brink of bankruptcy.
We’ve all seen it. A couple years of back to back successes, and owners feel invincible! The next thing you know, there is new equipment and buildings being added to the operation, fancy vacations being planned, and new personal expenditures (like houses, RV’s, and vehicles) being made like the lotto has just been won. Everyone who sees this opulence must surely believe that this business is very successful.
If owners (managers) are ill-equipped for the rapid success they’ve enjoyed, there is a likelihood that less-than-ideal decisions will be made in the future. As Marshall Goldsmith titled his bestselling book, What Got Your Here Won’t Get You There. Management has to keep up with the change that sustainable growth requires. This could include new knowledge/strategy/execution in areas like cash management, human resources, marketing, etc. Growth kills when management’s ability is stagnant in the face of growing complexity in business.
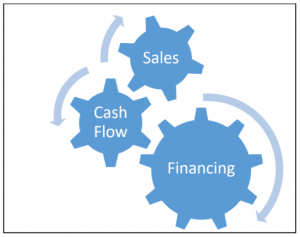
As sales grow, there is a need for more investment in the business (Eg. property/plant/equipment; labor; technology, etc.) to support the demand. That investment requires capital. Whether the capital is borrowed or sourced from within the business (usually taken out of working capital) has a major effect on the sustainability of the investment. Growth kills when, without a “home-run” or two, investment is pursued to the point that financing is maxed out and working capital is depleted.
What happens when more product is produced than the market can consume? A shift is made, and what once may have been a specialty item is now offered at a lower and lower price until supply has been consumed (see the “model year blowout” and virtually every car dealership every year.) A business that has enjoyed significant growth may decide to increase production based on past sales growth. Such a decision usually requires investment in the business (see the previous paragraph) and investment in inventory. Whether that inventory is raw material, or finished product remaining unsold, it is tying up working capital. How long can a business hold inventory before it converts that inventory to cash? If working capital is been reduced (see paragraph above) the answer is: not long.
Maybe the business is in a service industry. While there likely isn’t any inventory to have to manage, ramping up capacity (hiring & training staff, acquiring tools & equipment for staff, etc.) requires investment. These investments also carry an overhead expense (salaries & wages, utilities, depreciation, etc.) which becomes harder to pay for when market uptake is satiated. Growth kills when we assume the market will sustain our rapid growth for us.
Plan for Prosperity
What led to the recent success in business? Was it deliberate, planned, and executed…was it intentional growth? We recently discussed the ramifications of unintentional growth. Maybe this article should be titled (Unintentional) Growth Kills, but that probably would not have captured enough attention for you to even read it.
Growth Kills when the growth was unintentional and leads the ownership/management group to ignore the reality that (almost) all industries are cyclical. To say timing is everything does not give credit to important factors like strategy and execution, however an adequate strategy will give consideration to timing (to implement the growth strategy.)
It’s all connected. There is no magic bullet; one thing alone does not make success, and if it does, it’s “luck” and it’s short term because luck isn’t sustainable.