Innovation in Agriculture
Innovation
Noun | in·no·va·tion | \ˌi-nə-ˈvā-shən\
: a new idea, device, or method
: the act or process of introducing new ideas, devices, or methods
(Source: http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/innovation)
No one could ever decry the innovation of Canadian agriculture. Often looked favorably upon for
consistently being on the leading edge, Canadian farmers are typically the envy of other nations’
producers for our advanced processes and our willingness to constantly strive for something better.
Innovation takes many forms. It need not be monumental. It does not require a farm to re-identify itself.
While significant innovations like direct seeding and minimum tillage required major capital
investments, many others do not. If you’re like virtually every farm, there is innovation all around you…if
you take the time to look.
Consider the changes you’ve made to your farm since you began farming. Again, not just the big obvious
changes, but the little things too. The little things often make the biggest difference, and yet they are so
easy to overlook. Just think about the positive effect of doing your own grain moisture tests on farm.
I was having a conversation with a client recently about the impact of grain sampling and how the
grading at delivery points can sometimes be a bone of contention. He described in detail how and why
he samples every load as it is being augered from the bin onto the truck. This is an innovation he has
employed to ensure he has taken appropriate measures to protect himself during a dispute. It has paid
off several times in the past, and will likely be of continued value in the future.
An interesting conversation, to which I was privy, among a group of very progressive farmers was about
how each of them managed the challenge of “feeding their help” during harvest. Crews that number
well into the teens require more than a cooler full of sandwiches and donuts. One innovation that I
thought was most creative was the customization of an old Class C motorhome into a quasi food-truck.
While we automatically focus on operations when considering our success with innovation, we cannot
ignore the management side of business. A common issue among my clients this fall is land rent
renewals. Many of them are seeking better ways to access their rented land without taking on so much
risk with these high cost all cash arrangements. As with land prices, rents have also increased
substantially over the last several years (thank you Captain Obvious for contributing to this week’s
article.) Farmers, generally, are becoming less comfortable with the $70-$100+/ac they’ve added to
their LBF (Land, Buildings, Finance) costs for land rent over the years and are now recognizing that they
often can’t make money on that rented land. Unless you’re running a charity, one that benefits your
landlords, “re-think profit” becomes an innovation all on its own.
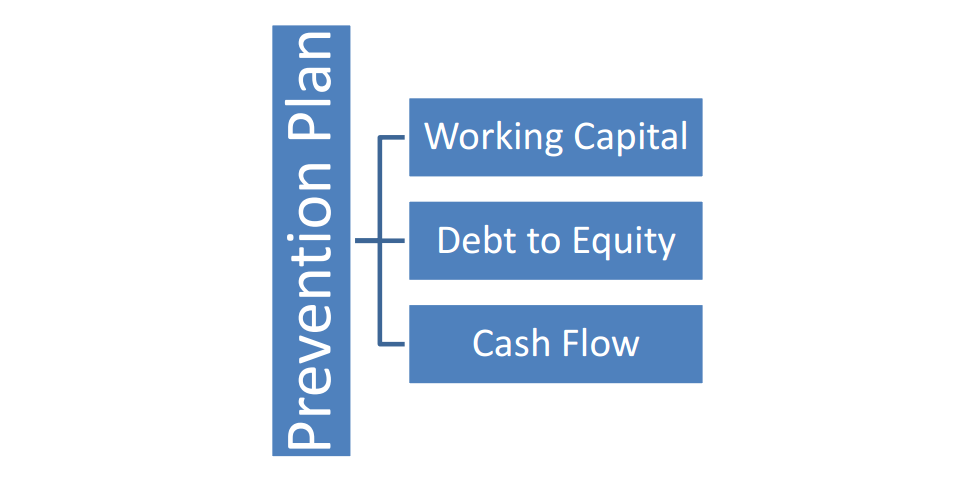
Innovation is refining your record keeping, automating your payroll services, or focusing on improving
your working capital. While innovation also includes variable rate, advanced water management, or
specialized grain monitoring systems, it need not always be BIG and OBVIOUS. I think the best
innovation for every farm is to examine how it views profit, growth, and wealth.
Direct Questions
How do you view profit, growth, and wealth? I define each as,
Wealth: – discretionary time.
Profit: – that what is required to fuel “wealth.”
Growth: – not necessarily “expansion.” Growth is innovation at any and all levels.
(Remember “always grow; grow all ways!”)
How can you bring about innovation in your management arsenal?
How does innovation make its way into your business? Do you invite it in, or does it have to force its way
in?
From the Home Quarter
I am a firm believer that change will continue to be rapid and drastic in the future. In terms of record
keeping and data management, it will one day be mandatory, so why not get on board before you’re
forced? Regarding my client’s issue on his grain sampling, I believe that future farmers will be forced to
manage their inventory similar to that of a food processor today. And if you have not heard the term
“social license” yet, then let this be the first. A farmer’s social license to farm could face scrutiny like
we’ve never seen before. All of this will require significant innovation. But, don’t fret over the big issues
yet. Start small with manageable innovations today.
Our proprietary Farm Profit Improvement Program™ includes analysis and advice on negotiating land
rental agreements. Please call or email for further details.