Financial Literacy Month
November is Financial Literacy Month, an initiative of The Financial Literacy Action Group which is “a
coalition of seven organizations that work to assist and improve the financial literacy of Canadians.”
http://www.financialliteracymonth.ca/About-FLAG/
Watching some news the other morning while having breakfast, I saw a financial commentator discuss 3
simple financial questions to which Canadians have averaged 1.8 out of 3 correct answers. And trust me,
these were SIMPLE questions. But anyone who knows me knows that I will always acknowledge that
“you don’t know what you don’t know.”
That being said, there is no shame in not knowing what you don’t know. It is when you don’t know what
you should know that risk is increased. Here is a short quiz for you to take regarding your farm financial
literacy for the occasion of Financial Literacy Month.
1. Your current assets are MORE than your current liabilities. This means your working capital is
a. Negative
b. Positive
c. I don’t know
2. Your contingency fund (emergency cash) has a balance of $50,000 in a savings account earning
1% interest per year. If inflation is currently 2%, then the net real value (the buying power) of
your contingency fund after 1 year is
a. More than $50,000
b. Exactly the same as the start: $50,000
c. Less than $50,000
3. The tractor you bought last year for $200,000 can be sold today for $215,000. You’ve claimed
$30,000 in depreciation on that tractor, meaning it has a book value of $170,000. You’ve just
sold the tractor for $215,000, and now you will have a
a. $45,000 capital gain
b. $15,000 capital gain
c. $30,000 recaptured CCA
d. Both b) and c)
e. None of the above
4. My banker is always in a hurry to see my financial statements because
a. He’s looking for a way to increase my interest rates
b. They need to ensure I’m still a good credit risk
c. She’s trying to lend me more money
5. I’m a farmer; I don’t need to know all those ratios and analysis and stuff.
a. True
b. False
While these questions I’ve posed to you aren’t the simplest questions that everyone should know, they
will create a benchmark for you to get an idea of what you do know and where your mindset is. At the
end of the day, it is up to you to determine if and how you will tackle the imperative task of advancing
your farm financial management. In a bit of shameless self-promotion, I have developed a classroom
seminar titled Advancing Your Farm Financial Management.
https://fbdi.gov.sk.ca/LP_LearningActivityDetail.aspx?id=Q6UJ9A03H15A&area=Financial+Management
It is a one day commitment. It has been developed for the farm business owner who wants to take his
basic financial knowledge to an intermediate level. It has been approved for reimbursement under the
Farm Business Development Initiative. http://www.agriculture.gov.sk.ca/GF2-FBDI
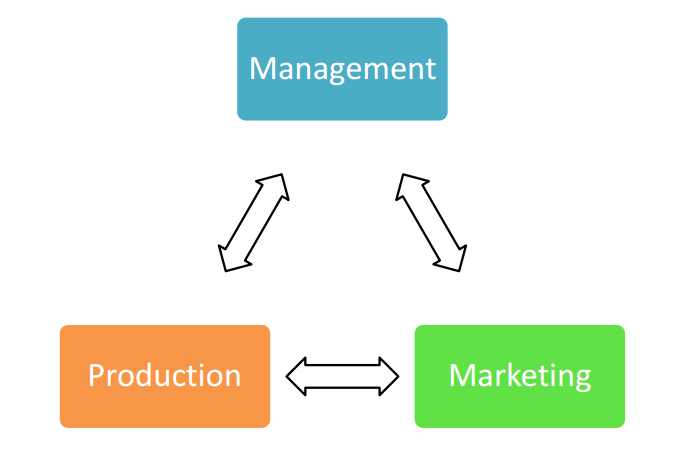
Course participants will learn what is important to their banker and why. They will develop an
appreciation for the risks all farmers face, plus the risks to their specific farm and how to mitigate those
risks. Each participant will go home having built the foundation of their own personalized financial
management plan. And the best part: lunch is on me!
Direct Questions
When it comes to financial jargon, the importance of financial management and how to use the
information, if you don’t know what you don’t know, who will you call for help?
I hear it is not uncommon to pay upwards of $10,000-$20,000 to your equipment dealer for them to go
through your combine to ensure everything is up to par. What is it worth to do the same for your farm’s
finances? Do you do it as often as you do for the combine?
From the Home Quarter
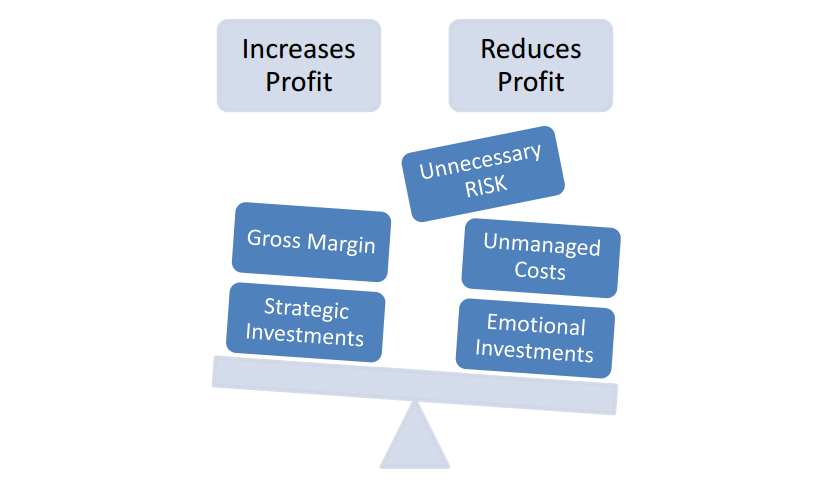
In a business with as much inherent risk as production agriculture, ignoring certain aspects of your
business increases risk exponentially. And whether that ignoring stems from a lack of interest or
understanding or time, the risk does not simply go away because it has little attention paid to it…in fact,
it grows. To create an analogy, ignoring risk is like ignoring a weed in your field: pay little attention to it,
it still grows; deal with it right away, and you increase your probability of a successful crop.
In the spirit of Financial Literacy Month, I challenge everyone to become more fluent in one new
financial term each week in November.
And for the answers to the quiz above, send me an email.
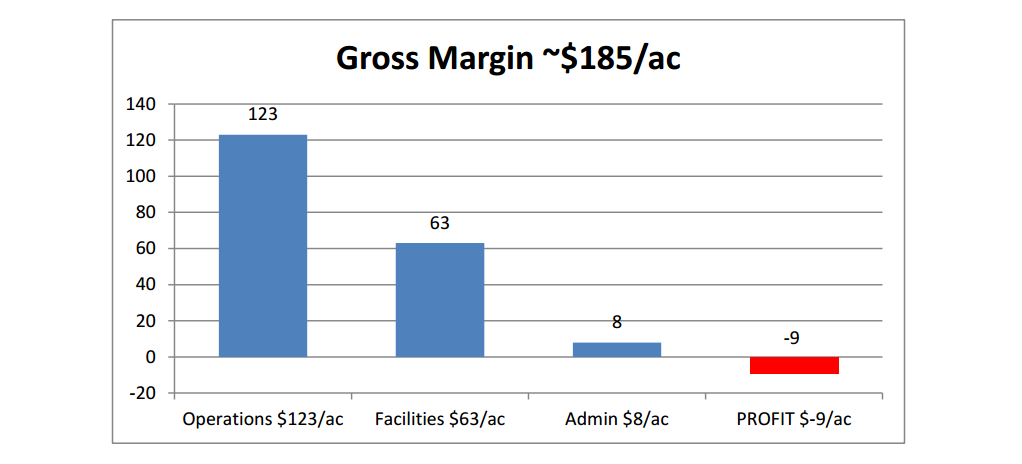
Our proprietary Farm Financial Analysis provides you with a straight-forward, easy to read report of
your farm’s financial position with focus on areas of strength, caution, and danger. Call or email for
more details.